
January 2026
Two randomized trials examine whether anticoagulation can be safely discontinued after successful catheter ablation
The issue: One-year success rates of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation range from 50 - 85% and decline over time. Many patients hope to stop anticoagulation after ablation, but the risks and benefits of this decision have not been clearly defined.
Why these studies matter: The ALONE-AF and OCEAN studies were designed to evaluate the risks and benefits of stopping anticoagulation after successful catheter ablation. They also provided guidance on what defines successful ablation.
Primary care relevance: The studies provide data for making an informed decision on stopping anticoagulation and determining which patients are candidates.
January 2026
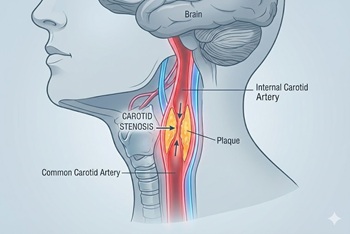
New randomized trial compares carotid stenting and endarterectomy to intensive medical management
The issue: In the U.S., most asymptomatic high-grade (≥70%) carotid stenosis is treated with revascularization (stenting or endarterectomy). However, the risks and benefits of this approach, and how it compares with contemporary medical therapy, have never been evaluated in a clinical trial.
Why this study matters: The CREST-2 study provides the first modern evidence comparing carotid stenting and endarterectomy to intensive medical management for asymptomatic carotid stenosis.
Primary care relevance: Providers now have good data to counsel patients on the risks and benefits of stenting, endarterectomy, and medical management of asymptomatic carotid stenosis.
December 2025

DECAF trial challenges long-standing recommendations to avoid coffee
The issue: Patients with atrial fibrillation are routinely advised to avoid caffeinated beverages, but evidence supporting this recommendation has been inconsistent.
Why this study matters: The DECAF randomized clinical trial compared continuing caffeinated coffee consumption to abstinence in patients with atrial fibrillation who underwent successful electrical cardioversion.
Primary care relevance: Provides guidance on counseling patients with atrial fibrillation about coffee consumption.
November 2025
Recent trials question routine long-term beta-blocker use after MI
The issue: Beta-blockers are routinely recommended for all post-MI patients, but this practice is based on trials predating modern revascularization and intensive secondary prevention.
Why this study matters: Four recent randomized trials have evaluated the long-term benefit of beta-blockers in post-MI patients with preserved LVEF.
Primary care relevance: Provides guidance on continuing beta-blockers in post-MI patients with preserved LVEF.
October 2025
The HI-PRO trial randomized patients with provoked VTE and minor chronic risk factors to 12 months of apixaban or placebo after completing at least 3 months of anticoagulation.
The issue: Current guidelines recommend 3 months of anticoagulation for provoked VTE; the role of extended therapy in patients with ongoing risk factors is unclear.
Why this study matters: The trial evaluated the long-term benefit of extended anticoagulation in patients with provoked VTE and minor chronic risk factors.
Primary care relevance: Provides guidance on extending anticoagulation in patients with provoked VTE and minor chronic risk factors.
October 2025
Study finds higher potassium targets are beneficial in patients with ICDs and CVD
The issue: Patients with ICDs and cardiovascular disease are at risk for ventricular arrhythmias; potassium levels may influence this risk.
Why this study matters: The trial evaluated the benefit of targeting high-normal potassium levels (4.5–5.0 mEq/L) in patients with ICDs and CVD.
Primary care relevance: Provides guidance on adjusting potassium supplements and medications in patients with ICDs and CVD.
September 2025
The guidelines are thorough, but are they practical?
The issue: Primary aldosteronism is an underdiagnosed cause of hypertension; screening and confirmatory testing vary in practice.
Primary care relevance: Updated guidance helps identify patients with resistant or hypokalemic hypertension who may benefit from screening and targeted treatment.
July 2025
First non-SGLT2 inhibitor approved for HFpEF
The issue: HFpEF has limited pharmacologic options; SGLT2 inhibitors are approved but additional therapies are needed.
Why this study matters: Finerenone (Kerendia), a nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, was approved for HFpEF based on the FINEARTS-HF study, showing reduced worsening heart failure events.
Primary care relevance: Providers now have a third drug option for HFpEF and the first non-SGLT2 inhibitor for this condition.
June 2025
Albumin-adjusted calcium formulas are less accurate than unadjusted levels for calcium status
The issue: Corrected (albumin-adjusted) calcium is widely used in hypoalbuminemia, but accuracy has been questioned.
Why this study matters: It evaluates the accuracy of albumin-adjusted calcium formulas for determining calcium status.
Primary care relevance: Relying on corrected calcium may be misleading; unadjusted levels or ionized calcium may be more reliable when assessing calcium status.
May 2025
Another study finds clopidogrel is better than aspirin in South Koreans with chronic coronary disease
The issue: Antiplatelet choice for chronic coronary disease remains debated; aspirin has been standard but clopidogrel has been compared in several trials.
Why this study matters: A trial in South Korean patients with CCD found clopidogrel superior to aspirin for cardiovascular outcomes.
Primary care relevance: Adds to the evidence base for antiplatelet selection in chronic coronary disease; although applicability may vary by population.
April 2025

The SOUL Study is a larger and longer version of a previous Rybelsus trial
The issue: Wegovy has been shown to reduce cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes; the effects of Rybelsus are unknown.
Why this study matters: The SOUL study evaluated the long-term benefit of Rybelsus in adults with type 2 diabetes and established or high cardiovascular risk.
Primary care relevance: Provides evidence on the benefits of Rybelsus for preventing cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes and established or high cardiovascular risk.
December 2024
BPROAD found intensive BP control reduced CVD in type 2 diabetes, contradicting ACCORD
The issue: Optimal blood pressure targets in type 2 diabetes have been debated; ACCORD suggested no benefit from intensive control, but newer evidence was needed.
Why this study matters: The BPROAD study found that intensive BP control (systolic <120 mmHg) significantly reduced cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes, contradicting the older ACCORD trial.
Primary care relevance: Updated evidence supports consideration of intensive BP targets in some patients with type 2 diabetes; guidelines may evolve.
December 2024

CLEAR study: colchicine failed to improve CVD outcomes in recent MI patients after PCI
The issue: Prior trials suggested colchicine could reduce cardiovascular events; the CLEAR study tested this in a different population.
Why this study matters: Despite prior positive studies, colchicine did not improve CVD outcomes in the CLEAR study, which included patients with recent MI who had undergone PCI; high dropout and factorial design may explain discrepant findings.
Primary care relevance: Colchicine for secondary CVD prevention is not supported by this trial; existing guidance may need to be revisited.
December 2024
Cross-sectional study finds secondary hypertension prevalent in 30% of hypertensive adults aged 18–40
The issue: Secondary hypertension is often underdiagnosed; prevalence in young adults was unclear.
Why this study matters: A cross-sectional study found secondary hypertension in about 30% of hypertensive adults aged 18 to 40, highlighting the importance of screening in younger patients.
Primary care relevance: Young adults with hypertension may warrant a higher index of suspicion for secondary causes and appropriate workup.